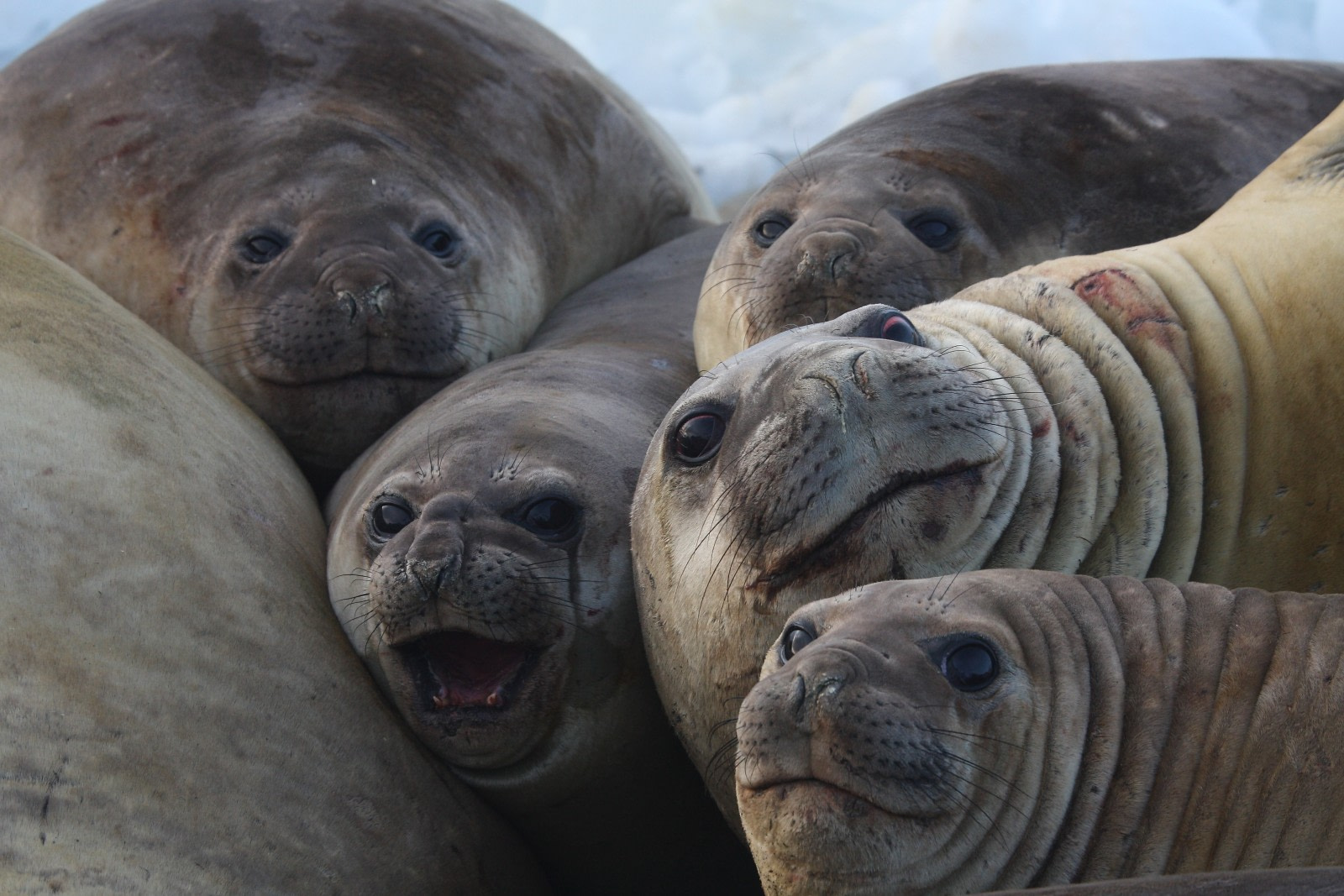
Southern elephant seals are the largest species of seal on the planet and a highlight among Antarctica cruise wildlife.
You can most often see southern elephant seals along the Antarctic coastline, dozing in the sun, nursing their pups, or swimming in the waters just off shore. And if you don’t see them first, you’ll almost certainly smell them.
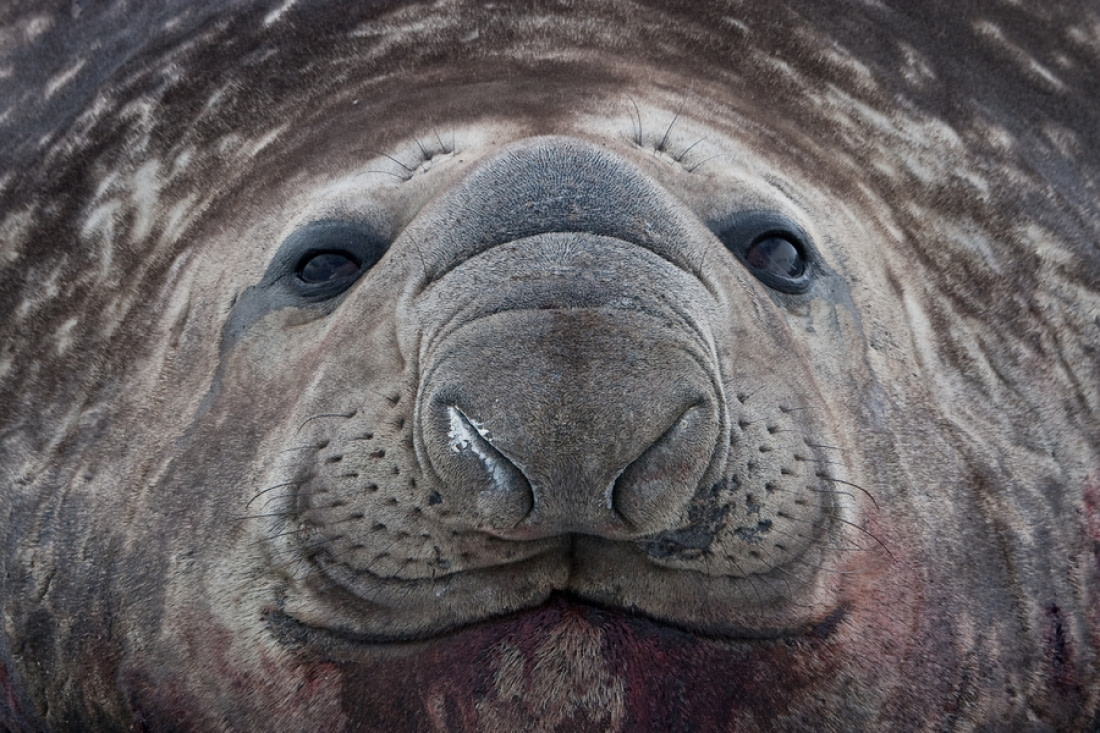

Southern elephant seals vs. northern elephant seals
At first glance, northern elephant seals and southern elephant seals appear quite similar.
They’re both large, loud, and (among males) share a distinctive elephant-like nose. There are two main differences, however, between the species.
The first difference is habitation range: Northern elephant seals range from the southern tip of Baja, Mexico, to the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. On the opposite end of the globe, southern elephant seals are restricted to the colder waters of the Southern Ocean.
The second difference is size: Southern elephant seals seriously outweigh their northern counterparts. Male southern elephant seals can reach up to 3,700 kg (8,150 pounds), while northern elephant seals usually only grow to about 2,300 kg (5,070 pounds).
Male adult southern elephant seals, or bulls, can be 4.2 to 5.8 meters (14 to 19 feet) long.
It may be that, at some point in their history, all elephant seals were one species. Over time, environmental factors like ocean temperature, food availability, predation, and geography may have caused them to diverge into the two distinct species alive today.
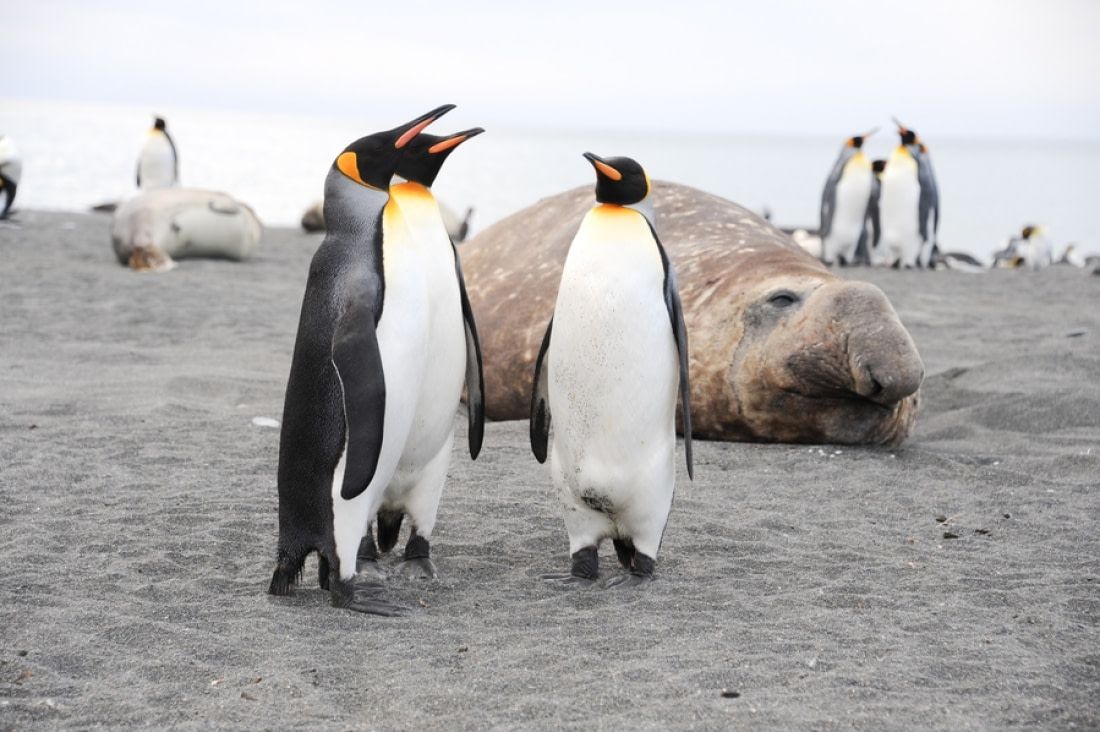

The deep dives of southern elephant seals
Southern elephant seals have been recorded diving up to 2,133 meters (7,000 feet) and can stay underwater for nearly two hours.
Their large eyes allow them to seek prey in areas with low light. When it gets dark, their sensitive vibrissae whiskers also let them probe the water for prey. Using their sharp teeth, southern elephant seals can dig through mud or snatch prey out of the water.
Southern elephant seal diet is largely composed of squid, mollusks, krill, cephalopods, and algae. They may eat more, but their long and deep dives make dietary studies difficult.
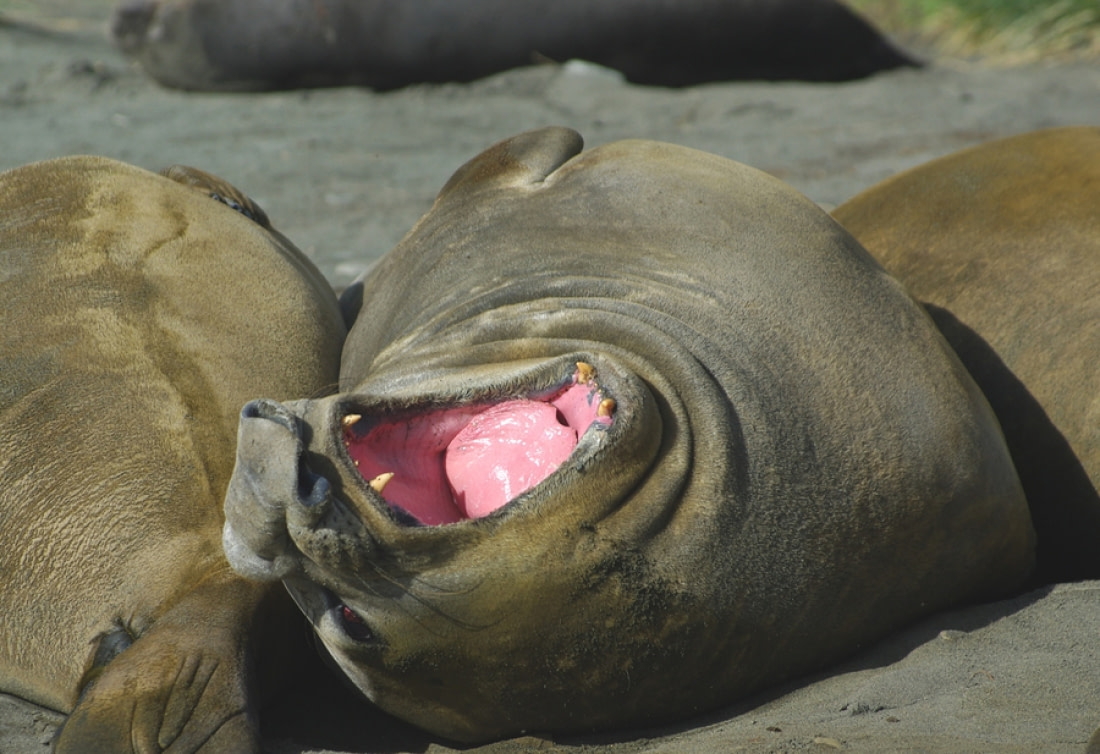

Southern elephant seal breeding season
The southern elephant seal breeding season, which lasts from August to November, is the best time to see these animals hauled out on land.
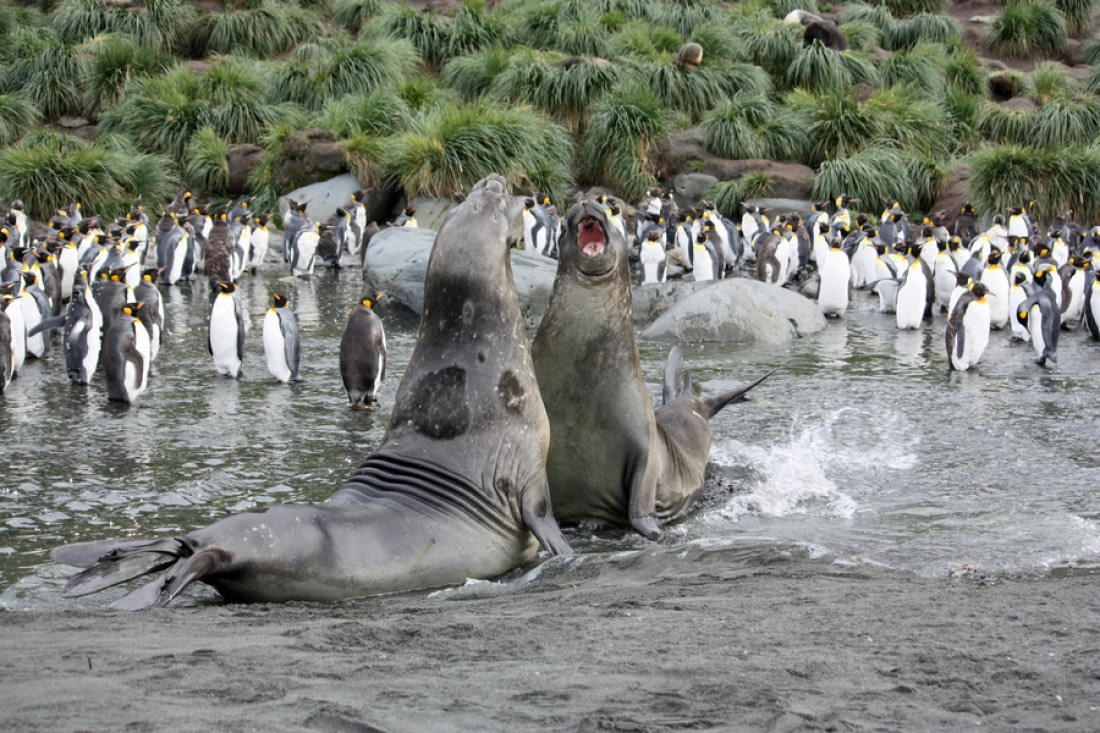
During this time, the larger males fight one another to establish dominance over a particular section of beach. Dominance fights can last for hours and end in serious injuries to both elephant seals. Vocalizations are also common during these fights and are amplified by inflating their trunk-like noses with air.
Once a beach master has been established, he will gather a harem of 40 to 50 females that he will vigilantly monitor and defend until the end of the breeding season. Female southern elephant seals give birth to one pup that they nurse for up to 23 days, then head back into open water to feed and regain energy. The pups, or weaners, are left to fend for themselves, congregating into pods for four to six weeks.
These weaner pods next face the dangerous task of leaving the beach and descending into the open ocean. Orcas, one of the only known predators of southern elephant seals, can be lethal adversaries during this vulnerable period.

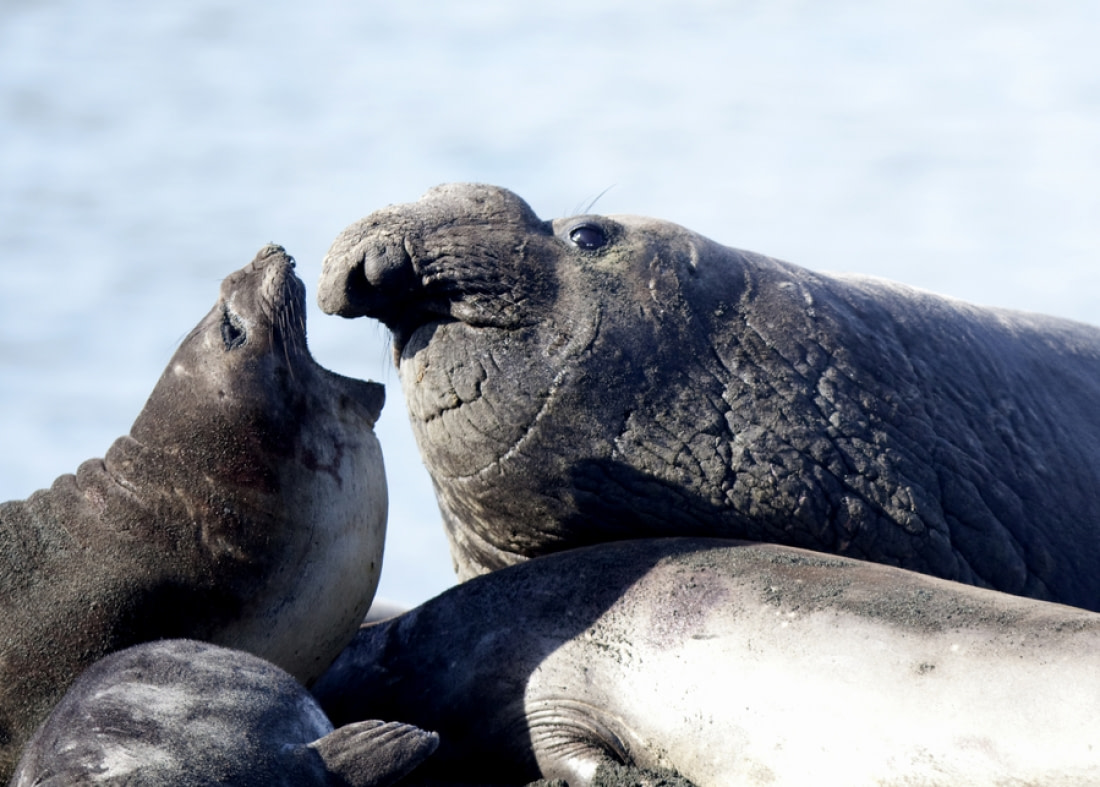
Working with southern elephant seals
On King George Island in the Antarctic Peninsula, southern elephant seals are monitored from October to March using non-invasive methods.
Every week, scientists at the Copacabana Field Camp walk along King George Island’s beaches and record how many southern elephant seals they see. Adults, sub-adults, young adults, and pups are included in the survey, along with their behaviors. Occasionally, southern elephant seals can be seen hauling their way through an entire penguin colony, disturbing everything in their path.
Slow though they move, southern elephant seal size alone poses a threat to unhatched penguin eggs and even adults. This is bad news for scientists trying to study the penguins, but it is also worth documenting these events.
On rare occasions, a southern elephant seal’s decision to haul out in the middle of a penguin colony has resulted in the failure of every one of the colony’s nests. Southern elephant seals can also be dangerous for scientists: If a southern elephant seal wakes up and sees an unfamiliar object, such as a scientist, walking towards them, they’ll open up their large mouths and display their many sharp teeth.
This is usually only meant as a warning, but if they feel especially threatened they’ll vocalize and advance.
At this point, it’s best for the scientist to abandon the survey and find a safe escape route. Southern elephant seals may seem slow, but they can move surprisingly fast (and cause a lot of damage) if they feel threatened.

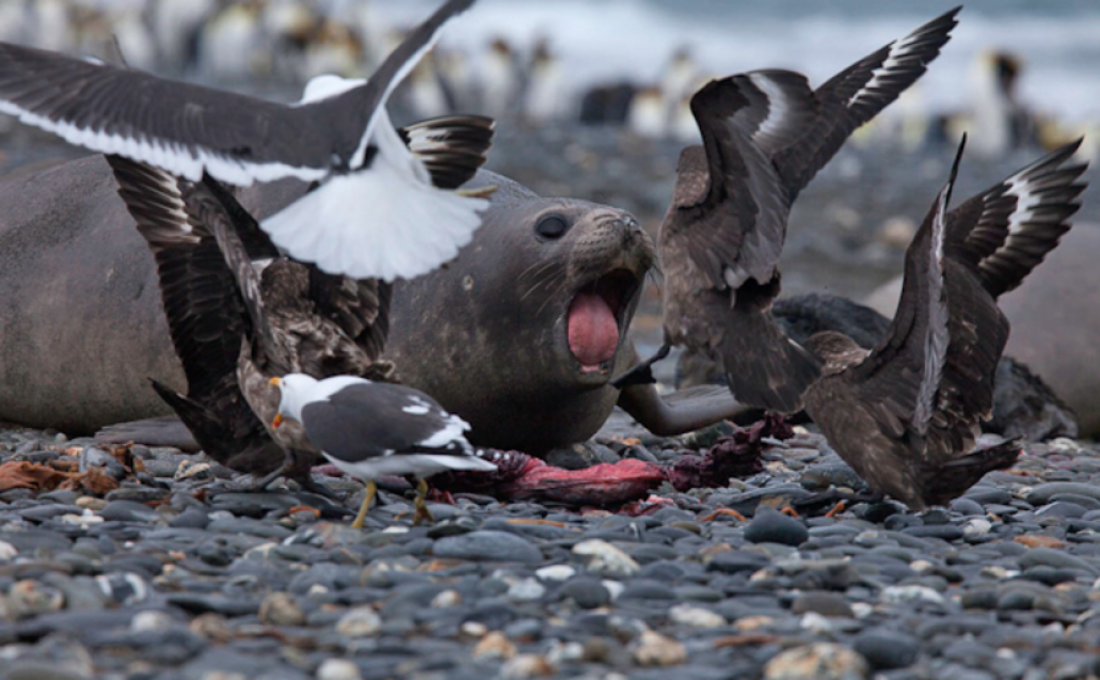
Southern elephant seal conservation concerns
Southern elephant seals were hunted nearly to extinction during the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, desired for their blubber.
In response to the decline of southern elephant seals and other marine mammals, conservation efforts such as the Marine Mammal Protection Act and Antarctic Treaty were passed. Southern elephant seals have since witnessed a significant increase in population.
But though they are no longer considered vulnerable, southern elephant seal populations have seen downward trends in the modern world.
Scientists predict that changing ocean temperatures have lead to a decrease in food availability for southern elephant seals. Even so, more concrete evidence concerning the unique diet and behavior of southern elephant seals is needed to help researchers understand how to better protect these giants of the sea.

Blog



Antarctica’s first Marine Protected Area

Polar Bear Primer: Eight Facts About the Arctic Wanderer

Shackleton’s Long-Lost Endurance Discovered in Antarctica

Orcas of the Polar Seas

The Arctic Hare: Easter Bunny

Arctic Seals

The disastrous expedition in the Arctic west

The Seasons of Antarctica: When to Visit and Why

Science of the Ross Ice Shelf

Port Pastimes: 7 Fun Things to Do in Longyearbyen

The World Is Changing for Greenland's Native Inuit People

North Norway, Northern Lights, and All the Pretty Whales

Greenland: East vs. West

A Look Into the International Research Stations of Antarctica

Scenes from St. Andrews Bay: 12 Pics of Penguins, Seals, and More

Arctic Foxes: Constant Gardeners of the Arctic

The Overlooked Treasures of Ascension Island

The Eight Albatrosses of Antarctica and the Sub-Antarctic

16 Conversation-Starting Svalbard Facts